HealthRite Medical Rehab offers Kinesio taping to treat pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, especially sports-related injuries. Kinesio taping helps to support muscle, remove congestion to the flow of body fluids, activate endogenous analgesic systems, and correct joint problems.
How does Kinesio Taping work?
The Kinesio Taping® (KT) Method is the rehabilitative application of Kinesio® Tape to facilitate the body’s natural healing process while providing support and stability to muscles and joints without restricting the body’s range of motion as well as providing extended soft tissue manipulation to prolong the benefits of manual therapy administered within the clinical setting.
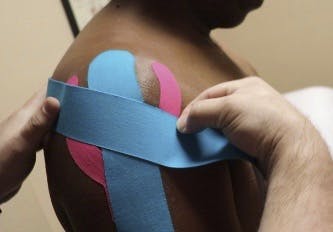
Kinesio® Tape is a latex-free, elastic porous cotton strip with an acrylic adhesive used for treating athletic injuries and a variety of other physical disorders.
It can also be left on for longer periods of time (up to 4 days) before reapplication is needed.
Kinesio® Tape is about as thick as human epidermis (skin) and is designed to mimic its elastic properties to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, relax muscles, enhance performance, and help with rehabilitation as well as supporting muscles during a sporting event.
For chronically injured or weakened muscles, needing support and full range of motion, the tape is applied with light tension, starting from the origin of the muscle and extending toward the tendons that hold the muscle to the bone.
How is Kinesio® Tape applied?
Kinesio® Tape is applied in five general cuts or techniques:
- The “Y” cut
- The “I” cut
- The “X” cut
- The “Fan” cut .
- The “Donut” cut
Benefits?
- Pain relief
- Improves ROM
- Improves joint stability
- Reduces muscle fatigue
- Improves muscle contraction of weakened muscle.
- Improves blood and lymphatic circulation.
- Supporting the muscle:
- Correcting joint problems
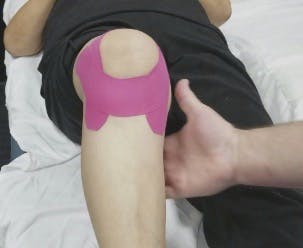
What conditions respond well to Kinesio taping?
- Sprains/ Strains
- Sciatica
- Low back/ Neck pain
- Shoulder/Knee Pain
- Fibromyalgia
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Joint Replacement
- Muscle Imbalance
- Rotator Cuff Syndrome
- Ligament/ Tendon/ Joint injuries
- Post op Knee/Shoulder surgery
